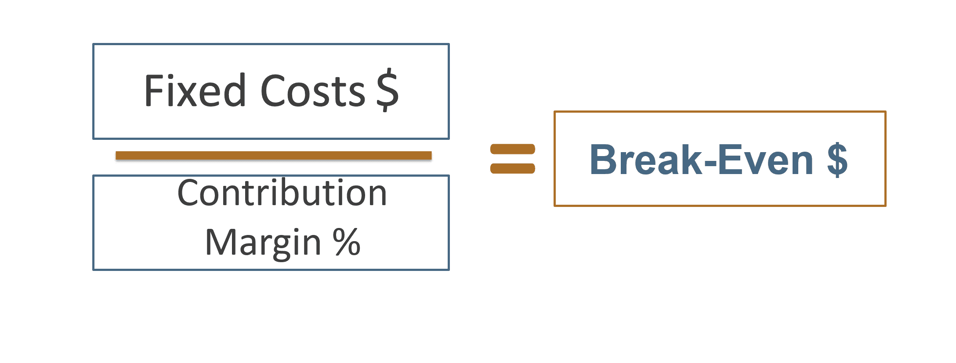
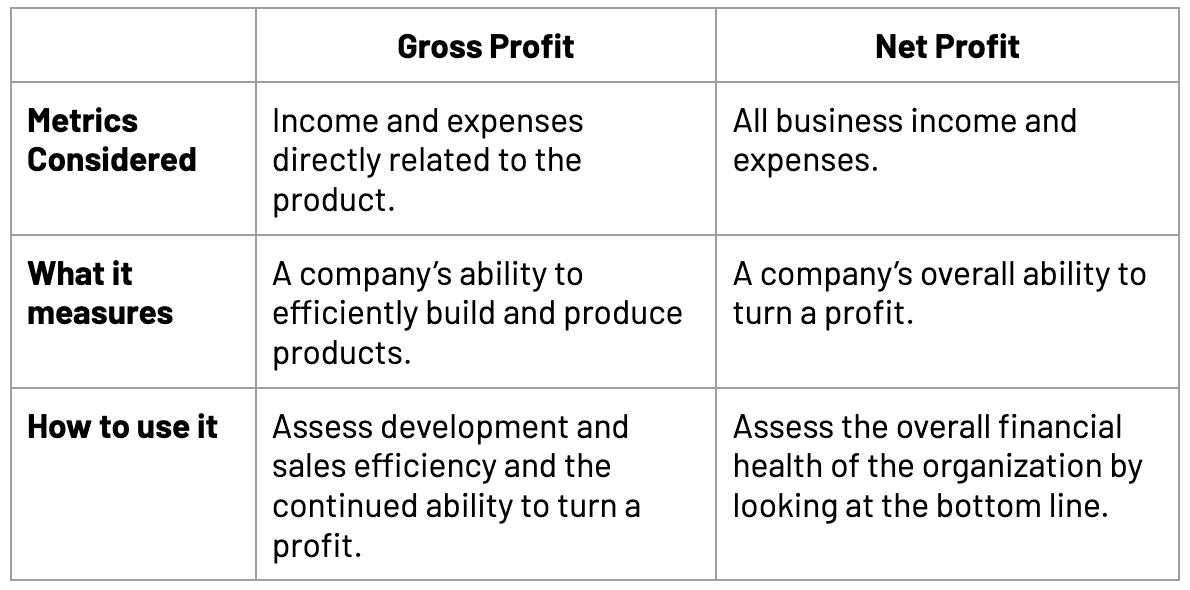
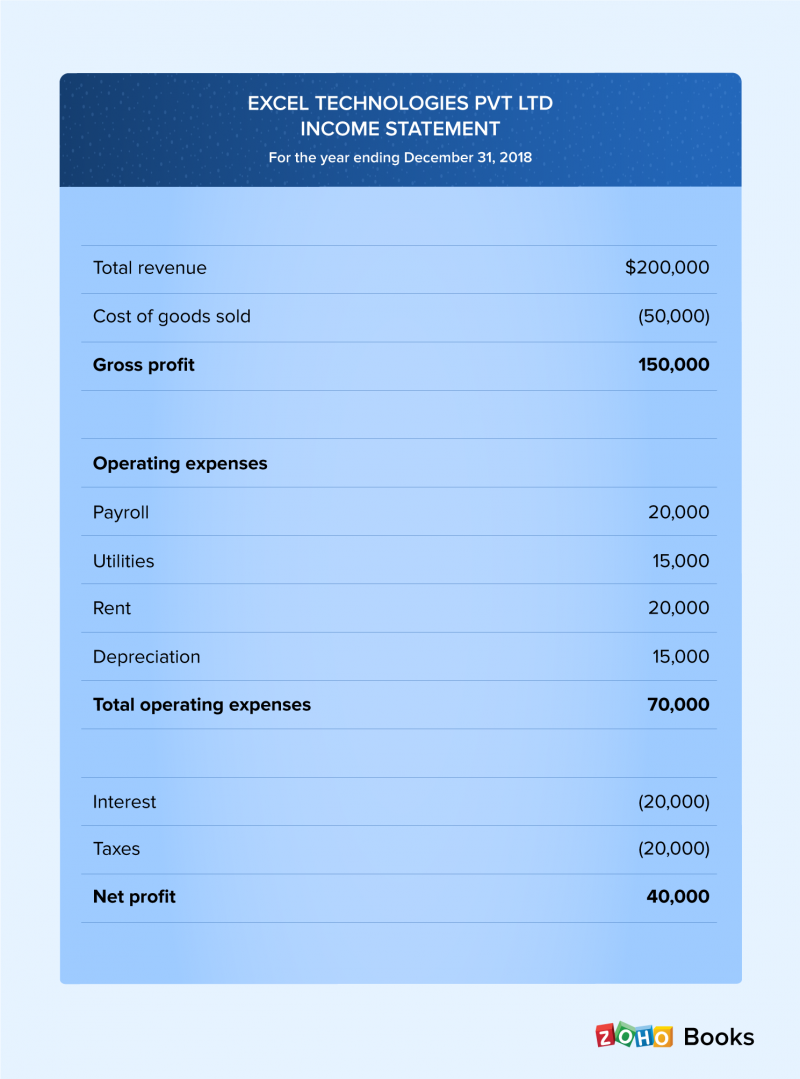
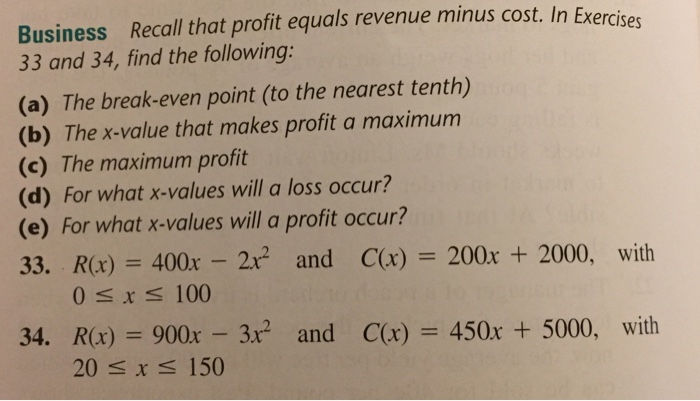Profit is equal to revenue minus cost, where revenue equals price times quantity of output, while cost equals the wage rate times employment (assuming wages are the only cost of production). Assume
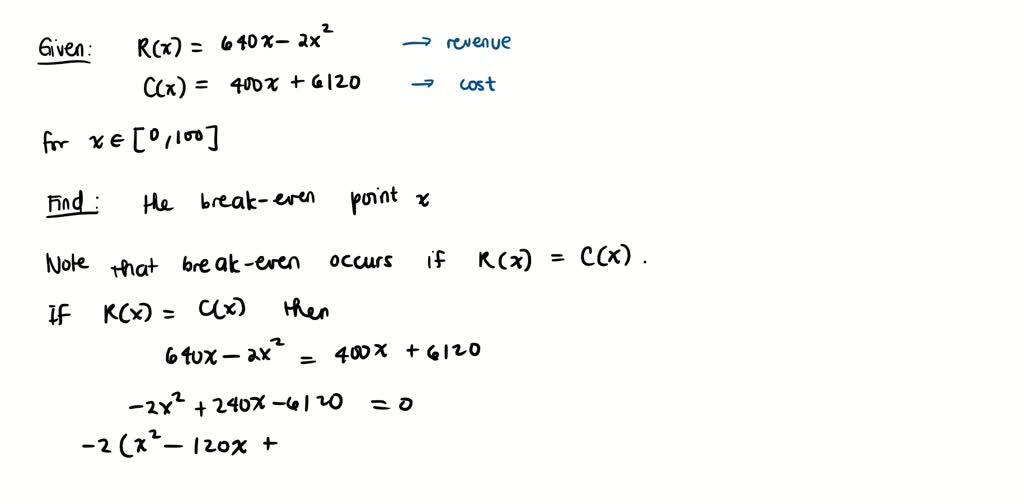
SOLVED: Recall that profit equals revenue minus cost. For the revenue and cost functions shown, answer parts (a) through (e) below. R(x)=640x-2x^2 and C(x)=400400x+6120, with 0 ≤ x ≤ 100 a- the