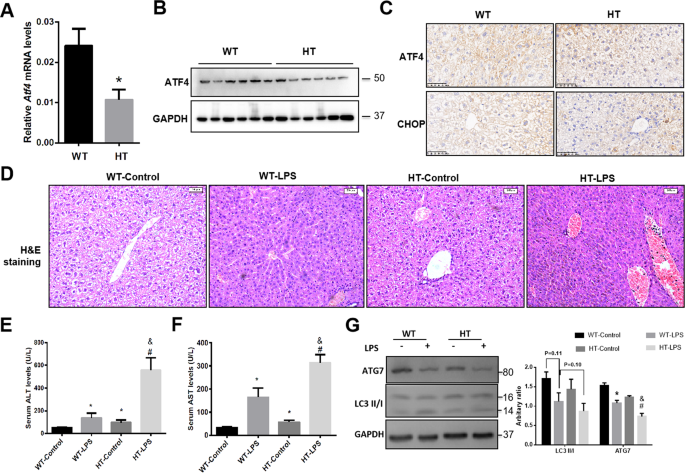
IL-22 ameliorates LPS-induced acute liver injury by autophagy activation through ATF4-ATG7 signaling | Cell Death & Disease

Qingchangligan formula attenuates the inflammatory response to protect the liver from acute failure induced by d-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide in mice - ScienceDirect
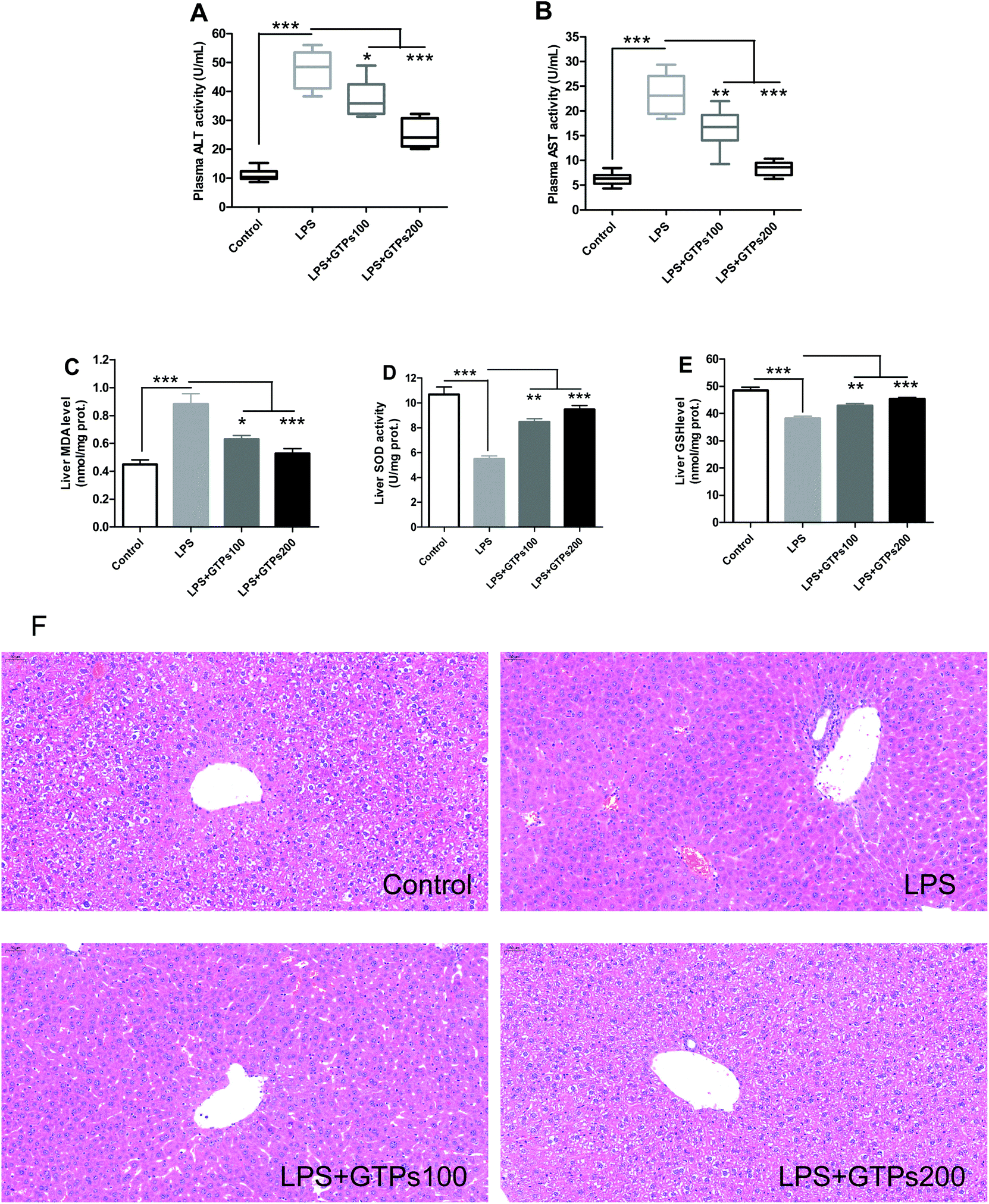
Green tea polyphenols prevent lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory liver injury in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation - Food & Function (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C9FO00572B
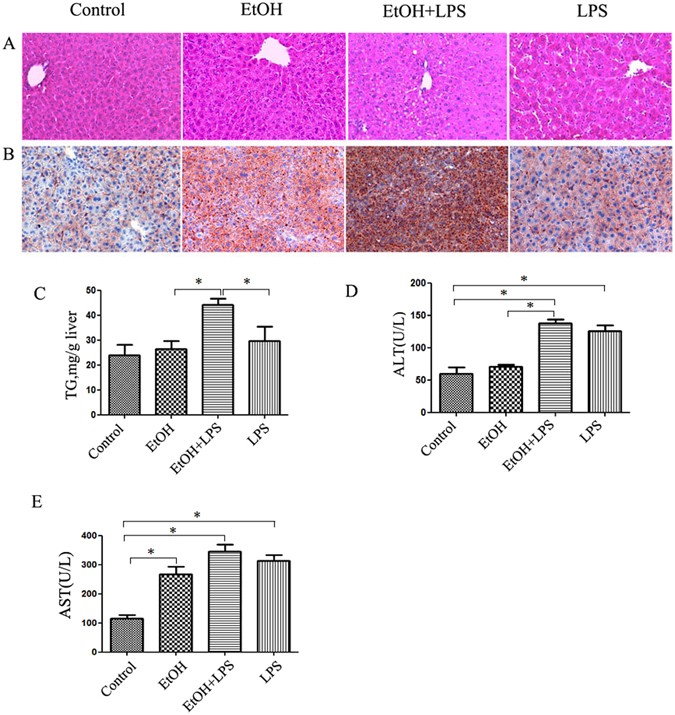
Activation of autophagy attenuates EtOH-LPS-induced hepatic steatosis and injury through MD2 associated TLR4 signaling | Scientific Reports
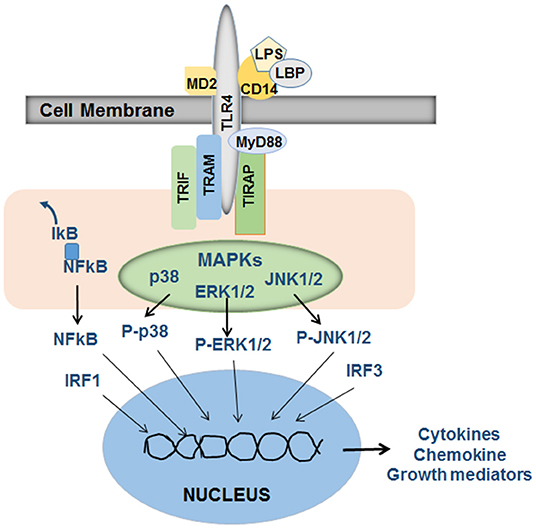
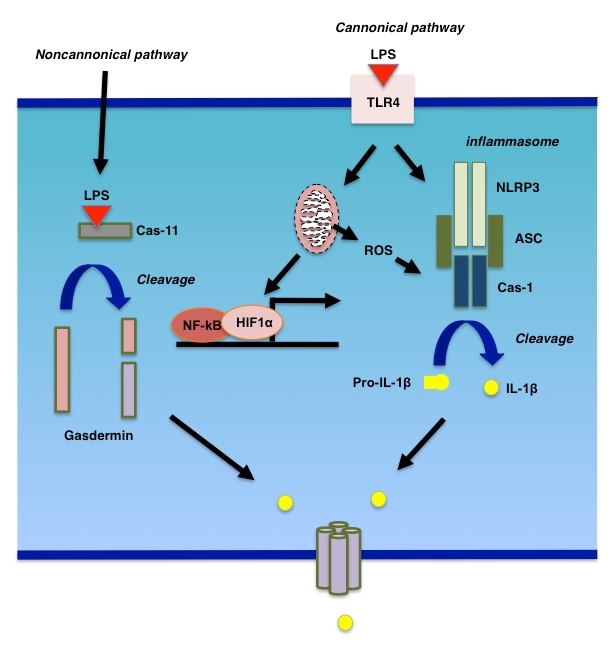
Frontiers | Pro- and Anti-fibrogenic Functions of Gram-Negative Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide in the Liver
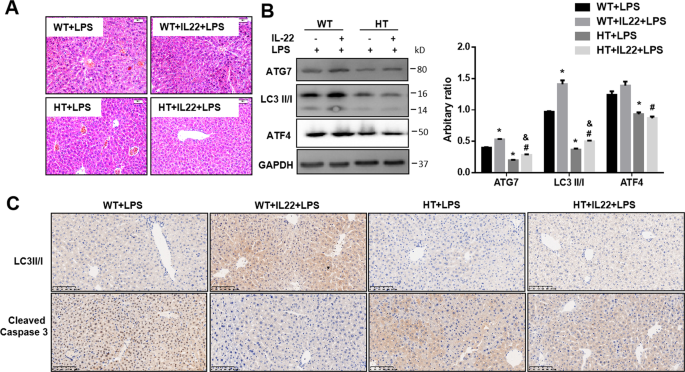
IL-22 ameliorates LPS-induced acute liver injury by autophagy activation through ATF4-ATG7 signaling | Cell Death & Disease
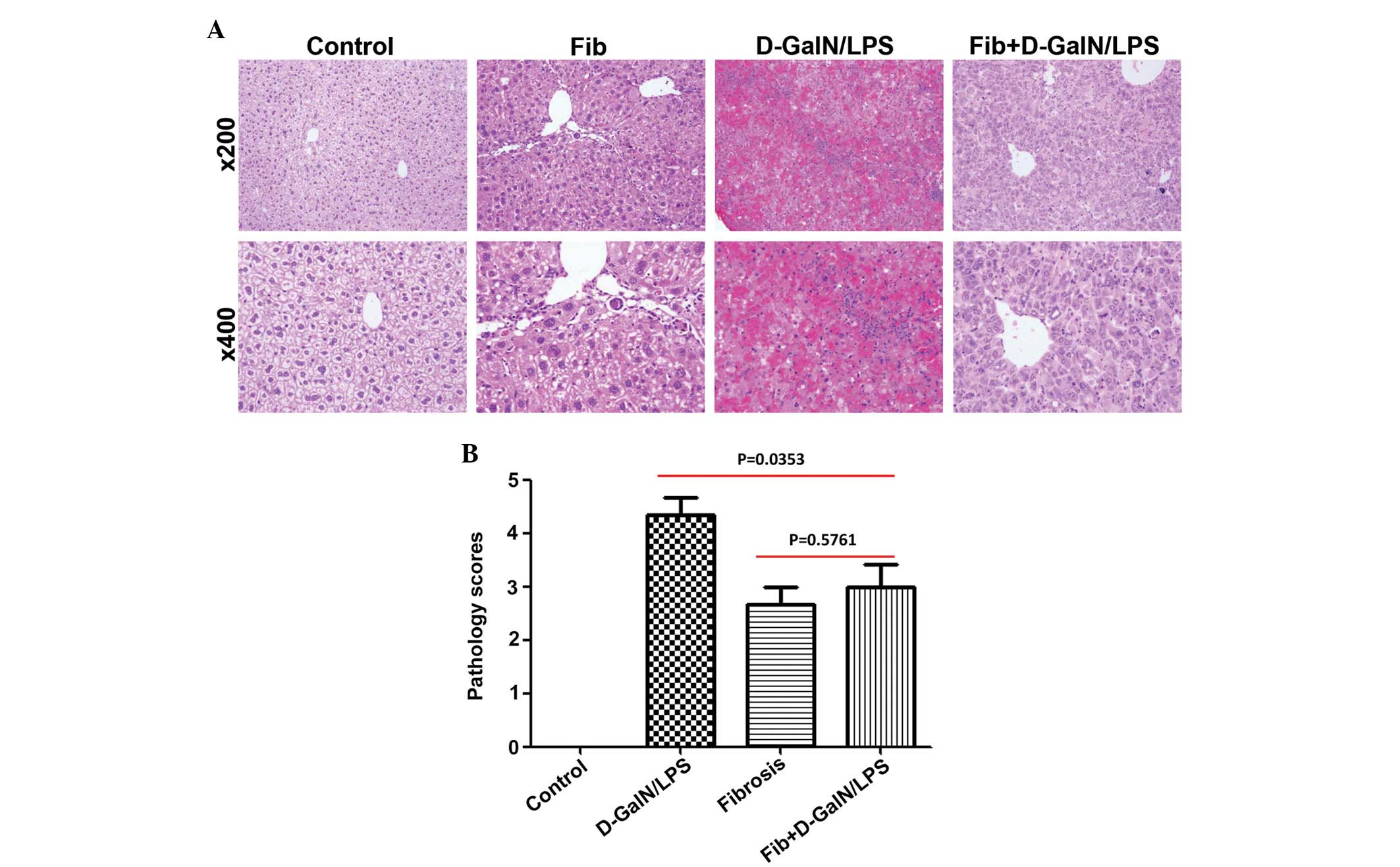
Inhibition of the translocation and extracellular release of high-mobility group box 1 alleviates liver damage in fibrotic mice in response to D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide challenge
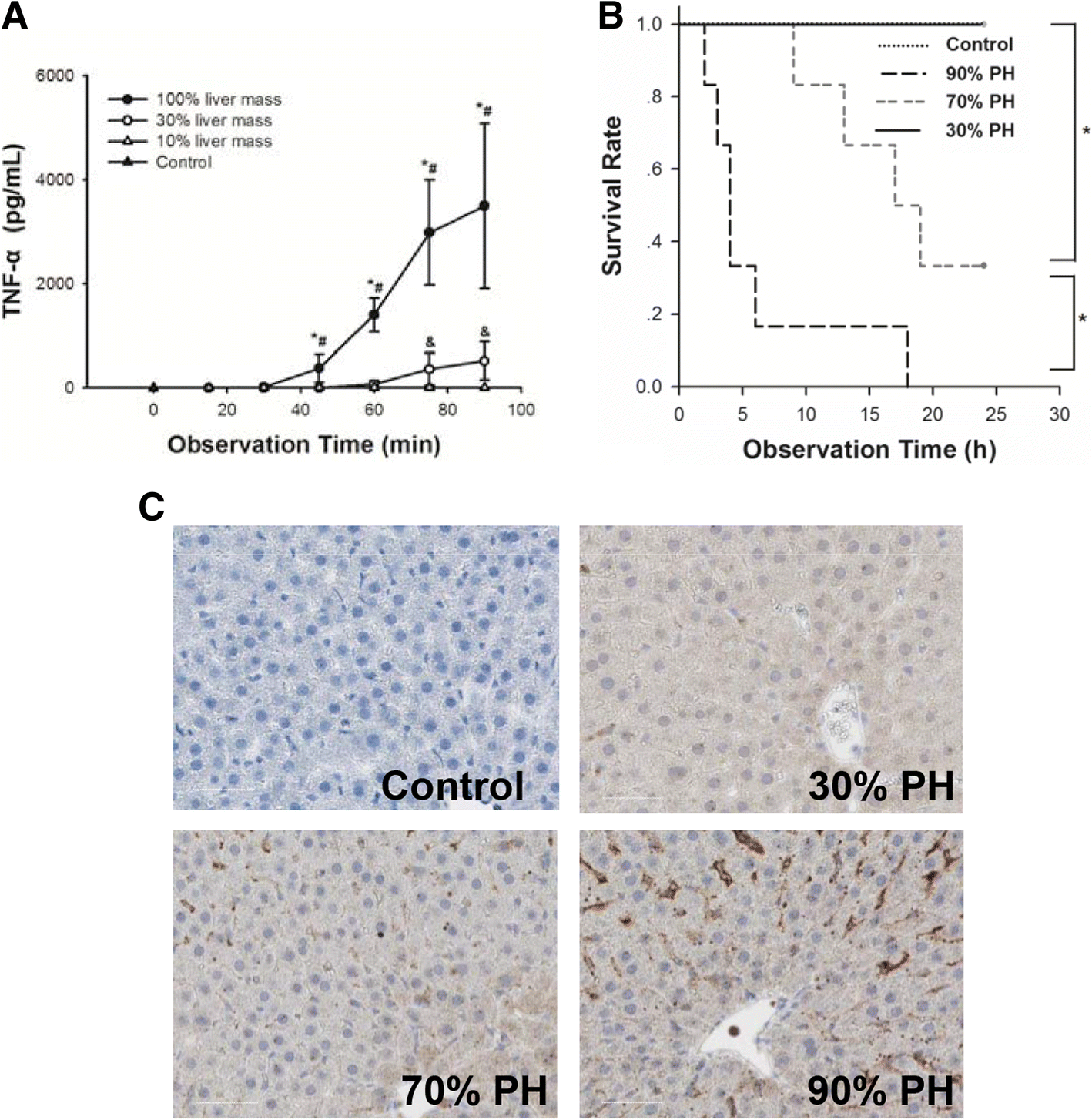
The severity of LPS induced inflammatory injury is negatively associated with the functional liver mass after LPS injection in rat model | Journal of Inflammation | Full Text
Co-administration of lipopolysaccharide and d-galactosamine induces genotoxicity in mouse liver | Scientific Reports

Qingchangligan formula attenuates the inflammatory response to protect the liver from acute failure induced by d-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide in mice - ScienceDirect

Investigation of protective effects of apilarnil against lipopolysaccharide induced liver injury in rats via TLR 4/ HMGB-1/ NF-κB pathway - ScienceDirect

Aging-related liver degeneration is associated with increased bacterial endotoxin and lipopolysaccharide binding protein levels | American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology
15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) prevents lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute liver injury | PLOS ONE
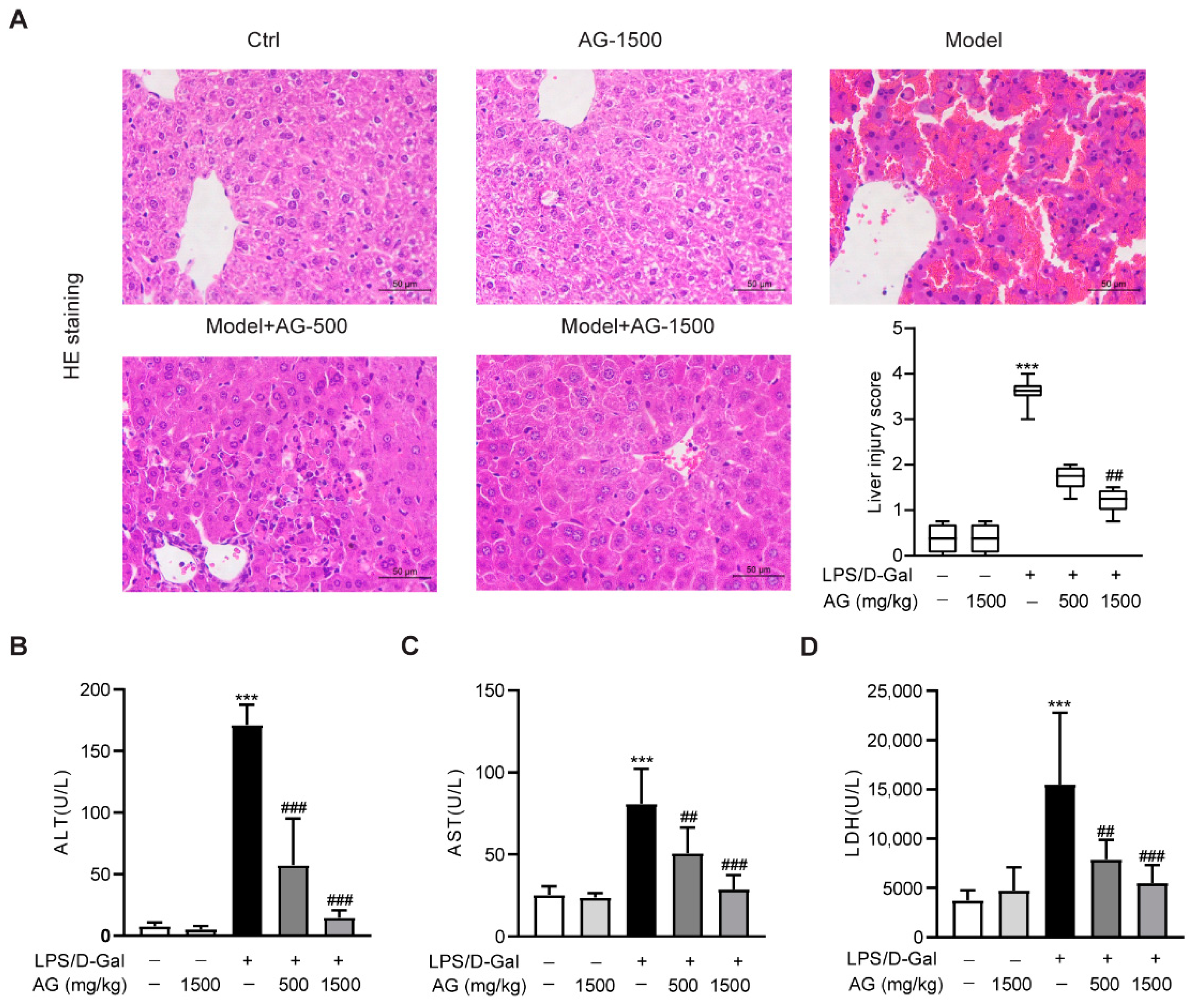
Antioxidants | Free Full-Text | Alanyl-Glutamine Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Injury in Mice via Alleviating Oxidative Stress, Inhibiting Inflammation, and Regulating Autophagy

Pathogens | Free Full-Text | rCsHscB Derived from Clonorchis sinensis: A Carcinogenic Liver Fluke Ameliorates LPS-Induced Acute Hepatic Injury by Repression of Inflammation
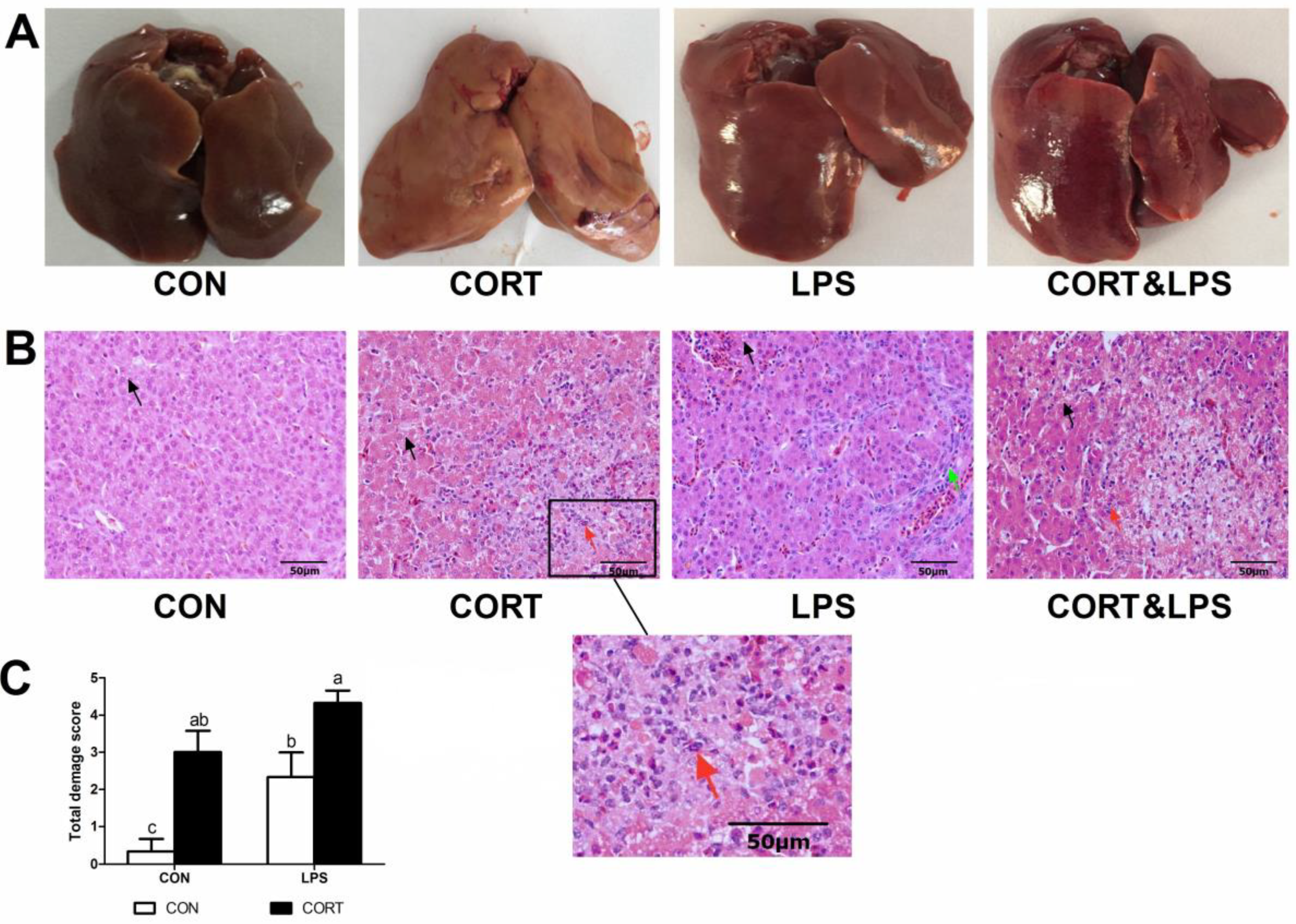
Animals | Free Full-Text | Hepatic Inflammatory Response to Exogenous LPS Challenge is Exacerbated in Broilers with Fatty Liver Disease

Alkaline phosphatase attenuates LPS-induced liver injury by regulating the miR-146a-related inflammatory pathway - ScienceDirect

Deletion of TLR4 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis | Acta Pharmacologica Sinica
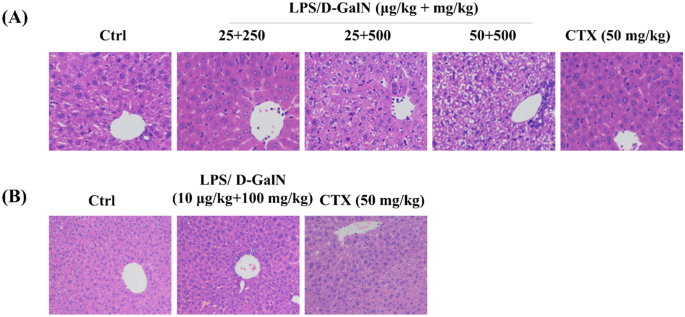
Lupeol ameliorates LPS/D-GalN induced acute hepatic damage by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress through TGFβ1-Nrf2 signal pathway - Figure f2 | Aging

Effects of simvastatin administration on rodents with lipopolysaccharide‐induced liver microvascular dysfunction - La Mura - 2013 - Hepatology - Wiley Online Library